|
I knew I knew her from somewhere, Ms Henrietta Lynch PhD, from the UCL Energy Institute. I had the feeling we’d sheltered together from the rain/police helicopters at a Climate Camp somewhere, but she was fairly convinced we’d crossed paths at the Frontline Club, where, if she was recalling correctly, I probably tried to pick an “difference of opinion” with somebody, which she would have remembered as more than a little awkward. |
|
Why ? Because when I’m surrounded by smart people displaying self-confidence, I sometimes feel pushed to try to irritate them out of any complacency they may be harbouring. Niceness can give me itchy feet, or rather emotional hives, and I don’t see why others should feel settled when I feel all scratchy. So here we were at a Parliamentary event, and I was on my best behaviour, neither challenging nor remonstrative, but all the same, I felt the urge to engage Henrietta in disagreement. It was nothing personal, really. It was all about cognition, perception – worldviews, even. After my usual gauche preamble, I snuck in with a barbed gambit, “The United Nations climate change process has completely failed.” A shadow of anxiety crossed her brow. “Oh, I wouldn’t say that”, said Henrietta Lynch. She went on to recount for me the validity of the UN climate talks, and how much further we are because of the Kyoto Protocol. “Ruined by Article 12”, I said, “…the flexible mechanisms”. She said I shouldn’t underestimate the effort that had gone into getting everybody into the room to talk about a response to climate change. I said, it would be useful if the delegates to the climate talks had power of some kind – executive decision-making status. Henrietta insisted that delegates to the climate talks do indeed have authority. I said that the really significant players, the oil and gas production companies, were not at the climate talks, and that there would be no progress until they were. I said that the last time the UN really consulted the oil and gas companies was in the 1990s, and the outcome of that was proposals for carbon trading and Carbon Capture and Storage. Each year, I said, the adminstration of the climate talks did the diplomatic equivalent of passing round a busker’s hat to the national delegations, begging for commitments to carbon emissions reductions. Besides leading to squabbling and game-playing, the country representatives do not even have the practical means of achieving these changes. Instead, I said, the energy production companies should be summoned to the climate talks and given obligations – to decarbonise the energy resources they sell, and to increase their production of renewable and sustainable energy. I said that without that, there will be no progress. Oil and gas companies always point to energy demand as their get-out-of-jail-free card – they insist that while the world demands fossil fuel energy, they, the energy resource companies, are being responsible in producing it. Their economists say that consumer behaviour can be modified by pricing carbon dioxide emissions, and yet the vast majority of the energy they supply is full of embedded carbon – there is no greener choice. They know that it is impossible to set an economically significant carbon price in any form, that there are too many forces against it, and that any behavioural “signal” from carbon pricing is likely to be swallowed up by volatility in the prices of fossil fuels, and tax revenue demands. Most crucially, the oil and gas companies know that fossil fuels will remain essential for transport vehicles for some time, as it will be a long, hard struggle to replace all the drive engines in the world, and high volumes of transport are essential because of the globalised nature of trade. Oil and gas companies have made token handwaving gestures towards sustainability. BP has spent roughly 5% of its annual budget on renewable energy, although it’s dropped its solar power division, and has now dropped its cellulosic ethanol facility. BP says that it will “instead will focus on research and development“. Research and development into what, precisely ? Improved oil and gas drilling for harsh environmental conditions like the Arctic Ocean or sub-sea high depth, high pressure fields ? How many renewable energy pipedreams are exhausted ? BP are willing to take competitors to court over biobutanol, but even advanced techniques to produce this biofuel are not yet commercialised. So, the oil and gas majors do not appear to be serious about renewable energy, but are they also in denial about fossil fuels ? All business school graduates, anybody who has studied for an MBA or attended an economics course, they all come out with the mantra that technology will deliver, that innovation in technology will race ahead of the problems. Yet, as the rolling disasters of the multiple Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear reactor accident and the continuing oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico from the blowout of the Horizon Deepwater drilling rig show, technological advancement ain’t what it used to be. Put not your faith in technology, for engineering may fail. For the oil and gas companies to be going after the development of unconventional fossil fuel resources is an unspoken, tacit admission of failure – not only of holding a bold vision of change, but also a demonstration of the failure of being able to increase production from discoveries of more conventional petroleum and Natural Gas. It is true that oil and gas exploration has improved, and that technology to drill for oil and gas has improved, but it could be said that the halting pace of technological advancement means that the growth in fossil fuel exploitation is not strong enough to meet projected demand. Technology does not always make things more efficient – the basic fossil fuel resources are getting much poorer, and perhaps scarcer. There is some evidence that global petroleum crude oil production rates have peaked, despite BP adding significant South American heavy oil fields to their annual Statistical Review of World Energy within the last few years. Some of the jitteriness in total production is down to geopolitical factors, like the chokehold that the United States has imposed on Iran via economic sanctions, and some of it is related to consumption patterns, but there is an element of resource failure, as indicated in this IMF report from last month :- “Over the past decade the world economy has experienced a persistent increase in oil prices. While part of this may have been due to continued rapid demand growth in emerging markets, stagnant supply also played a major role. Figure 1 shows the sequence of downward shifts in the trend growth rate of world oil production since the late 1960s. The latest trend break occurred in late 2005, when the average growth rate of 1.8 percent per annum of the 1981-2005 period could no longer be sustained, and production entered a fluctuating plateau that it has maintained ever since.” There is an increasing amount of evidence and projection of Peak Oil from diverse sources, so perhaps our attention should be drawn to it. If this type of analysis is to be trusted, regardless of whether the oil and gas companies pursue unconventional oil, change is inevitable. Bringing the oil and gas companies onto the world stage at the United Nations climate talks and demanding a reduction in fossil fuel production would be an straightford thing to make commitments to – as it is happening already. A huge facesaver in many respects – except that it does not answer the energy security question – how the world is going to be able to adapt to falling fossil fuel supplies. You see, besides Peak Oil, there are other peaks to contend with – it will not simply be a matter of exchanging one energy resource with another. Can the oil and gas companies hold on by selling us Natural Gas to replace failing oil ? Only if Natural Gas itself is not peaking. As the oil and gas companies drill deeper, more Natural Gas is likely to be found than petroleum oil, but because they are so often associated, Peak Oil is likely to be followed quite sharply by Peak Natural Gas. But does anybody in the oil and gas companies really know ? And if they did, would they be able to let their shareholders and world’s media know about it without their businesses crumbling ? What I want to know is : with all the skills of dialogue, collaboration, and facilitation that the human race has developed, why can Civil Society not engage the oil and gas companies in productive communication on these problems ? | |
Category: Global Warming
The Art of Non-Persuasion
|
I could never be in sales and marketing. I have a strong negative reaction to public relations, propaganda and the sticky, inauthentic charm of personal persuasion. Lead a horse to water, show them how lovely and sparkling it is, talk them through their appreciation of water, how it could benefit their lives, make them thirsty, stand by and observe as they start to lap it up. | |
|
One of the mnemonics of marketing is AIDA, which stands for Attention, Interest, Desire, Action, leading a “client” through the process, guiding a sale. Seize Attention. Create Interest. Inspire Desire. Precipitate Action. Some mindbenders insert the letter C for Commitment – hoping to be sure that Desire has turned into certain decision before permitting, allowing, enabling, contracting or encouraging the Action stage. You won’t get that kind of psychological plasticity nonsense from me. Right is right, and wrong is wrong, and ethics should be applied to every conversion of intent. In fact, the architect of a change of mind should be the mind who is changing – the marketeer or sales person should not proselytise, evangelise, lie, cheat, sneak, creep and massage until they have control. I refuse to do “Suggestive Sell”. I only do “Show and Tell”. I am quite observant, and so in interpersonal interactions I am very sensitive to rejection, the “no” forming in the mind of the other. I can sense when somebody is turned off by an idea or a proposal, sometimes even before they know it clearly themselves. I am habituated to detecting disinclination, and I am resigned to it. There is no bridge over the chasm of “no”. I know that marketing people are trained to not accept negative reactions they perceive – to keep pursuing the sale. But I don’t want to. I want to admit, permit, allow my correspondent to say “no” and mean “no”, and not be harrassed, deceived or cajoled to change it to a “yes”. I have been accused of being on the dark side – in my attempts to show and tell on climate change and renewable energy. Some assume that because I am part of the “communications team”, I am conducting a sales job. I’m not. My discovery becomes your discovery, but it’s not a constructed irreality. For many, it’s true that they believe they need to follow the path of public relations – deploying the “information deficit model” of communication – hierarchically patronising. Me, expert. You, poor unknowing punter. Me, inform you. You, believe, repent, be cleaned and change your ways. In this sense, communications experts have made climate change a religious cult. In energy futures, I meet so many who are wild-eyed, desperate to make a sale – those who have genuine knowledge of their subject – and who realise that their pitch is not strong enough in the eyes of others. It’s not just a question of money or funding. The engineers, often in large corporations, trying to make an impression on politicians. The consultants who are trying to influence companies and civil servants. The independent professionals trying to exert the wisdom of pragmatism and negotiated co-operation. The establishment trying to sell technical services. Those organisations and institutions playing with people – playing with belonging, with reputation, marketing outdated narratives. People who are in. People who are hands-off. People who are tipped and ditched. Those with connections who give the disconnected a small rocky platform. The awkwardness of invested power contending with radical outsiders. Denial of changing realities. The dearth of ready alternatives. Are you ready to be captured, used and discarded ? Chase government research and development grants. Steal your way into consultations. Play the game. Sell yourself. Dissociate and sell your soul. I have to face the fact that I do need to sell myself. I have to do it in a way which remains open and honest. To sell myself and my conceptual framework, my proposals for ways forward on energy and climate change, I need a product. My person is often not enough of a product to sell – I am neuro-atypical. My Curriculum Vitae CV in resume is not enough of a product to sell me. My performance in interviews and meetings is often not enough of a product. My weblog has never been a vehicle for sales. I didn’t want it to be – or to be seen as that – as I try to avoid deceit in communications. Change requires facilitation. You can’t just walk away when the non-persuasional communications dialogue challenge gets speared with distrust and dismissal. Somehow there has to be a way to present direction and decisions in a way that doesn’t have a shadow of evil hovering in the wings. “A moment to change it all, is all it takes to start anew. Why do I need to “sell” myself ? Why do I need to develop a product – a vehicle with which to sell myself ? 1. In order to be recognised, in order to be welcomed, invited to make a contribution to the development of low carbon energy, the optimisation of the use of energy, and effective climate change policy. 2. In order to put my internal motivations and drive to some practical use. To employ my human energy in the service of the future of energy engineering and energy systems. | |

| Something bizarre is happening in the sky, 4,000 metres above our heads. It’s getting unusually warm.
While we’ve been busy thanking Gaia that the surface temperatures in Greenland have dropped to ice-sustaining levels, we’ve taken our eyes off the rest of the Earth system. |
| Cold ground. But hot sky.
I suppose the key question is whether this heat burden will be circulated back around to ground level before the depths of Winter – in which case, it might defer the re-formation of the Arctic Sea Ice. Is it possible that at the same time as the Arctic Ocean is free of sea ice in Summer, that it’s significantly curtailed in Winter, too ? Is this the onset of a “new climate state” ? | |
[ UPDATE : The images and charts are current – meaning that the situation has changed since the post was written on 14 September 2012. Thus, if you try to tie the diagrams in with the text, it won’t make much sense. Apologies. ]
Bosworth: “We are not going soft on coal”
 | At the annual Stop Climate Chaos coalition chin-wag on Friday 20th July 2012, I joined a table discussion led by Tony Bosworth of the environmental group Friends of the Earth.
He was laying out plans for a campaign focus on the risks and limitations of developing shale gas production in the United Kingdom. |
|
During open questions, I put it to him that a focus on shale gas was liable to lay Friends of the Earth open to accusations of taking the pressure off high carbon fuels such as coal. He said that he had already encountered that accusation, but emphasised that the shale gas licencing rounds are frontier – policy is actively being decided and is still open to resolution on issues of contention. Placing emphasis on critiquing this fossil fuel resource and its exploitation is therefore timely and highly appropriate. But he wanted to be clear that “we are not going soft on coal”. I suggested that some experts are downplaying the risks of shale gas development because of the limitations of the resource – because shale gas could only contribute a few percent of national fuel provision, some think is is unwise to concentrate so much campaign effort on resisting its development. Bosworth countered this by saying that in the near future, the British Geological Survey are expected to revise their estimates of shale gas resource upwards by a very significant amount. He quoted one source as claiming that the UK could have around 55 years of shale gas resource within its borders. I showed some scepticism about this, posing the question “But can it be mined at any significant rate ?” It is a very common public relations trick to mention the total estimated size of a fossil fuel resource without also giving an estimate of how fast it can be extracted – leading to entirely mistaken conclusions about how useful a field, well or strata can be. Tony Bosworth said that shale gas reserve estimates keep changing all the time. The estimate for shale gas reserves in Poland have just been revised downwards, and the Marcellus Shale in the United States of America has also been re-assessed negatively. Bosworth said that although campaigners who are fighting shale gas development had found it useful to communicate the local environmental damage caused by shale gas extraction – such as ozone pollution, traffic noise, water pollution and extraction, landscape clearance – the best argument against shale gas production was the climate change emissions one. He said academics are still being recruited to fight on both sides of the question of whether the lifecycle emissions of shale gas are higher than for coal, but that it was becoming clear that so-called “fugitive emissions” – where gas unintentionally escapes from well works and pipeline networks – is the key global warming risk from shale gas. Opinion around the table was that the local environmental factors associated with shale gas extraction may be the way to draw the most attention from people – as these would be experienced personally. The problem with centring on this argument is that the main route of communication about these problems, the film Gasland, has been counter-spun by an industry-backed film “Truthland”. The Royal Society recently pronounced shale gas extraction acceptable as long as appropriate consideration was paid to following regulatory control, but even cautious development of unconventional fossil fuels does not answer the climate change implications. There is also the extreme irony that those who oppose wind farm development on the basis of “industrialisation of the landscape” can also be the same group of people who are in favour of the development of shale gas extraction – arguably doing more, and more permanently, to destroy the scenery by deforestation, water resource sequestration and toxification of soils, air and water. Tony Bosworth told the group about the Friends of the Earth campaign to encourage Local Authorities to declare themselves “Frack-Free Zones” (in a similar way to the “Fair Trade Towns” campaign that was previously so successful). He said that FoE would be asking supporters to demand that their local governments had a “No Fracking” policy in their Local Plans. It was suggested in the discussion group that with the current economic slowdown and austerity measures, that Local Authorities may not have the capacity to do this. Tony Bosworth suggested that in this case, it might be worth addressing the issue to church parish councils, who can be very powerful in local matters. It was pointed out that frequently, parish councils have been busy declaring themselves “Wind Free Zones”. It was considered that it would be ineffective to attempt to fight shale gas production on a site-by-site direct action basis as the amount of land in the UK that has already and will soon be licenced for shale gas exploration made this impossible. Besides which, people often had very low awareness of the potential problems of shale gas extraction and the disruption and pollution it could bring to their areas – so local support for direct action could be poor. One interesting suggestion was to create a map of the United Kingdom showing the watersheds where people get their tap supplies from superimposed on where the proposed shale gas exploration areas are likely to be – to allow people to understand that even if they live far away from shale gas production, their drinking water supplies could be impacted. In summary, there are several key public relations fronts on which the nascent shale gas “industry” are fighting. They have been trying to seed doubt on low estimates of actual shale gas production potential – they have been hyping the potentially massive “gamechanging” resource assessments, without clear evidence of how accessible these resources are. They have also been pouring scorn on the evidence of how much damage shale gas could do to local environments. And they have also been promoting academic research that could be seen to make their case that shale gas is less climate-damaging than other energy resources. Shale gas, and the issue of the risks of hydraulic fracturing for unconventional fossil fuels, is likely to remain a hot ecological topic. Putting effort into resisting its expansion is highly appropriate in the British context, where the industry is fledgeling, and those who are accusing Friends of the Earth and others of acting as “useful idiots” for the ambitions of the coal industry just haven’t taken a look at the wider implications. If shale gas is permitted dirty development rights, then that would open the gateway for even more polluting unconventional fossil fuel extraction, such as oil shale and underground coal gasification, and that really would be a major win for the coal industry. Friends of the Earth Briefing : Shale gas : energy solution or fracking hell ? | |
George Monbiot : Peak Agitation
My electronic mail inbox and Twitter “social media” timeline are full of people sparking and foaming about George Monbiot’s latest kow-tow to American academia. Apparently, he has discarded the evidence of many, many researchers, energy engineers and market players and poured luke-warm, regurgitated scorn on the evidence and inevitability of “Peak Oil”.
The level of agitation contradicting his stance has reached a new peak – in fact, I think I might claim this as “Peak Agitation”.
Here is just one example from Paul Mobbs, author of “Energy Beyond Oil”, and a multi-talented, multi-sectoral educator and researcher.
I initially read it in my inbox and nearly fell of my chair gobsmacked. When I had recovered from being astonished, and asked Mobbsey if I could quote him, perhaps anonymously, he wrote back :-
“No, you can quite clearly and boldly attach my name and email address to it ! And perhaps ask George for a response ?”
Sadly, George Monbiot appears to have jammed his thumbs in his ears as regards my commentary, so he is very unlikely to read this or become aware of the strength of opposition to his new positioning. But anyway – here’s for what’s it’s worth (and when it comes from Paul Mobbs, it’s worth a great deal) :-
Re: Peak oil – we were wrong. When the facts change we must change.
Hi all,
I’ve sat patiently through the various emails between you all — mainly to
take soundings of where you’re all at on this matter. In addition, over the
last few days I’ve separately received four dozen or so emails all asking
to “take on” Monbiot. I wasn’t going to reply because I’ve so many more
pressing matters to take care of, but given the weight of demands I can’t
avoid it.
I don’t see any point in “taking on” Monbiot; the points he raises, and the
debate that he has initiated, are so off beam compared to the basis of the
issues involved that it there’s no point proceeding along that line of
thought. You can’t answer a question if the question itself is not
understood!!
Let’s get one thing straight — present economic difficulties are not simply
to do with “oil”, but with the more general issue of “limits to growth”.
That’s a complex interaction of resource production, thermodynamics,
technology, and relating all of these together, economic theory. Reducing
this just to an issue of oil or carbon will fail to answer why the trends
we see emerging today are taking place. Instead we have to look towards a
process which sees energy, resources, technology and human economics as a
single system.
The problem with this whole debate is that those involved — Monbiot
included — only have the vaguest understanding of how resource depletion
interacts with the human economy. And in a similar way, the wider
environment movement has been wholly compromised by its failure to engage
with the debate over ecological limits as part of their promotion of
alternative lifestyles. Unless you are prepared to adapt to the reality of
what the “limits” issues portends for the human economy, you’re not going
to make any progress on this matter.
Monbiot’s greatest mistake is to try and associate peak oil and climate
change. They are wholly different issues. In fact, over the last few years,
one of the greatest mistakes by the environment movement generally (and
Monbiot is an exemplar of this) has been to reduce all issues to one
metric/indicator — carbon. This “carbonism” has distorted the nature of
the debate over human development/progress, and in the process the
“business as usual” fossil-fuelled supertanker has been allowed to thunder
on regardless because solving carbon emissions is a fundamentally different
type of problem to solving the issue of resource/energy depletion.
Carbon emissions are a secondary effect of economic activity. It is
incidental to the economic process, even when measures such as carbon
markets are applied. Provided we’re not worried about the cost, we can use
technological measures to abate emissions — and government/industry have
used this as a filibuster to market a technological agenda in response and
thus ignore the basic incompatibility of economic growth with the
ecological limits of the Earth’s biosphere. As far as I am concerned, many
in mainstream environmentalism have been complicit in that process; and
have failed to provide the example and leadership necessary to initiate a
debate on the true alternatives to yet more intense/complex
industrialisation and globalisation.
In contrast, physical energy supply is different because it’s a prerequisite
of economic growth — you can’t have economic activity without a
qualitatively sufficient energy supply (yes, the “quality” of the energy is
just as important as the physical scale of supply). About half of all
growth is the value of new energy supply added to the economy, and another
fifth is the result of energy efficiency — the traditional measures of
capital and labour respectively make up a tenth and fifth of growth. As yet
mainstream economic theory refuses to internalise the issue of energy
quality, and the effect of falling energy/resource returns, even though this
is demonstrably one of the failing aspects of our current economic model
(debt is the other, and that’s an even more complex matter to explore if
we’re looking at inter-generational effects).
The fact that all commodity prices have been rising along with growth for
the past decade — a phenomena directly related to the human system hitting
the “limits to growth” — is one of the major factors driving current
economic difficulties. Arguably we’ve been hitting the “limits” since the
late 70s. The difficulty in explaining that on a political stage is that
we’re talking about processes which operate over decades and centuries, not
over campaign cycles or political terms of office. As a result, due to the
impatience of the modern political/media agenda, the political debate over
limits has suffered because commentators always take too short-term a
viewpoint. Monbiot’s recent conversion on nuclear and peak oil is such an
example, and is at the heart of the report Monbiot cites in justification of
his views — a report, not coincidentally, written by a long-term opponent
of peak oil theory, working for lobby groups who promote business-as-usual
solutions to ecological issues.
Likewise, because the neo-classical economists who advise governments and
corporations don’t believe in the concept of “limits”, the measures they’ve
adopted to try and solve the problem (e.g. quantitative easing) are not
helping the problem, but merely forestall the inevitable collapse. For
example, we can’t borrow money today to spur a recovery if there will be
insufficient growth in the future to pay for that debt. Basically, whilst you
may theoretically borrow money from your grandchildren, you can’t borrow
the energy that future economic growth requires to generate that money if
it doesn’t exist to be used at that future date. Perhaps more perversely, a
large proportion of the economic actors who have expressed support for
limits are not advocating ecological solutions to the problem, they’re
cashing-in by trying to advise people how to make money out of economic
catastrophe.
Carbon emissions and resource depletion are a function of economic growth.
There is an absolute correlation between growth and carbon emissions. I
don’t just mean that emissions and the rate of depletion fall during
recessions — and thus “recessions are good for the environment”. If you
look at the rate of growth in emissions over the last 50 years, the change
in energy prices has a correlation to changes in carbon emissions as the
price of fuel influences economic activity. That’s why carbon emissions
broke with their historic trend, halving their previous growth rate, after
the oil crisis of the 1970s; and why they then rebounded as energy prices
fell during the 90s.
The idea that we can “decarbonise” the economy and continue just as before
is fundamentally flawed. I know some of you will scream and howl at this
idea, but if you look at the research on the interaction between energy and
economic productivity there is no other conclusion. Due to their high
energy density and relative ease of use, all fossil fuels have an economic
advantage over all the alternatives. That said, as conventional oil and gas
deplete, and “unconventional” sources with far lower energy returns are
brought into the market, that differential is decreasing — but we won’t
reach general parity with renewables for another decade or two.
Note also this has nothing to do with subsidies, or industrial power —
it’s a basic physical fact that the energy density of renewables is lower
than the historic value of fossil fuels. On a level playing field, renewable
energy costs more and has a lower return on investment than fossil fuels.
We do have the technology to develop a predominantly renewable human
economy, but the economic basis of such a system will be wholly different to
that we live within today. Unless you are prepared to reform the economic
process alongside changing the resource base of society, we’ll never
see any realistic change because all such “ecological” viewpoints are
inconsistent with the values at the heart of modern capitalism (that’s not
a political point either, it’s just a fact based upon how these systems
must operate). E.g., when the Mail/Telegraph trumpet that more wind power
will cost more and lower growth/competitiveness, they’re right — but the
issue here is not the facts about wind, it’s that the theory/expectation of
continued growth, which they are measuring the performance of wind against,
is itself no longer supported by the physical fundamentals of the human
economy.
The present problem is not simply “peak oil”. Even if volumetric production
remained constant, due to the falling level of energy return on investment
of all fossil fuels the effects of rising prices and falling systemic
efficiency will still disrupt the economic cycle (albeit at a slower rate
than when it is tied to a simultaneous volumetric reduction). Allied to the
problems with the supply of many industrial minerals, especially the
minerals which are key to the latest energy and industrial process/energy
technologies (e.g. rare earths, indium, gallium, etc.), what we have is a
recipe for a general systems failure in the operation of the human system.
And again, that’s not related to climate change, or simple lack of energy,
but because of the systemic complexity of modern human society, and what
happens to any complex system when it is perturbed by external factors.
The worst thing which can happen right now — even if it were possible,
which is entirely doubtful — would be a “return to growth”. The idea of
“green growth”, within the norms of neo-classical economics, is even more
fallacious due to the differing thermodynamic factors driving that system.
Instead what we have to concentrate upon is changing the political economy
of the human system to internalise the issue of limits. At present, apart
from a few scientists and green economists on the sidelines, no one is
seriously putting that point of view — not even the Green Party. And as I
perceive it from talking to people about this for the last 12 years, that’s
for a very simple reason… it’s not what people, especially the political
establishment, want to hear.
Rio+20 was an absolute failure. In fact what annoyed me the most was that
the media kept talking about the “second” Rio conference, when in fact it
was the third UNCED conference in the Stockholm conference in ’72. If you
contrast 1972 with 2012, the results of this years deliberations were worse
than the policies sketched out in the 70s ! Seriously, the environment
movement is being trounced, and as I see it that’s because they have lost
the intellectual and theoretical rigour that it possessed in the 70s and
80s. Rather than having a clear alternative vision, what they promote is
“the same but different”. Once environmentalism became a media campaign
about differing consumption options, rather than an absolute framework for
evaluating the effects of consumption, it lost its ability to dictate the
agenda — because its the ability to look forward and observe/anticipate
trends unfolding, however unwelcome those truths might be, which gives
groups political power.
Politicians have lost control of the economy because their materialist
ambitions no longer fit to the extant reality of the economic process. This
outcome was foreseen over 40 years ago by economists like Georgescu-Roegen
and Boulding but ignored, even amongst many liberals and especially the
left, for political reasons. These same principles, based around the issue
of limits, were also the founding reality of the modern environment
movement — but over the last 20 years the movement has lost this basic
grounding in physics and economics as it has moved towards an
aspirationally materialist agenda (green consumerism/sustainable
consumption, etc.).
Unless you’re prepared to talk about limits to growth, and the fact that
the economic theories developed over two centuries of unconstrained
expansion now have no relevance to a system constrained by physical limits,
then you will not solve this problem. Just as with Monbiot’s “change” on
the issue of nuclear, his failure is a matter of basic theory and
methodological frameworks, not of facts or data. Unfortunately people keep
throwing data at each other without considering that the framework within
which those facts are considered and understood has changed, and that
consequently their conclusions may not be correct; and until the movement
accepts that the rules governing the system have changed we’ll not make
progress in advancing viable solutions.
To conclude then, Monbiot’s mistake isn’t about peak oil, or climate
change, it’s a failure to internalise the physical realities of the
“limits” now driving the human system. Unless you consider the interaction
of energy, economics and pollution, any abstractions you draw about each of
those factors individually will fail to tell you how the system as a whole
is functioning. Those limits might dictate the end of “growth economics”,
but they DO NOT dictate the end of “human development”. There are many ways
we can address our present economic and environmental difficulties, but that
cannot take place unless we accept that changing our material ambitions is
a prerequisite of that process.
Let’s be clear here. The principles which drive the economy today would be
wholly alien to Adam Smith, John Stuart Mill and others who first laid down
the rules of the system two centuries ago. Likewise Marxism and similarly
derived ideas have no validity either because they were generated during an
era when there were no constraining limits. There is no “going back” to
previous theories/ideologies on this issue because we face a scenario today
which humans society — with the exception of those ancient societies who
experienced ecological overshoot (Rome, Mayans, Easter Islanders, etc.) —
have never had to face before.
We have to move forward, to evaluate and understand is the role of
ecological limits within the future human economic process and how this
changes our advocacy of “solutions”. That debate should be at the heart of
the environment movement, and the issue of limits should lead all
discussions about all environmental issues — not green/sustainable
consumerism and other measures which seek to reassure and pacify affluent
consumers. That said, especially given the demographic skew within
membership of the environment movement, we have to begin by being honest
with ourselves in accepting the “limits agenda” and what it means for the
make-up of our own lives.
In the final analysis, you cannot be an environmentalist unless you accept
and promote the idea of limits. That was at the heart of the movement from
the early 70s, and if we want to present a viable alternative to disaster
capitalism then that is once again what we must develop and promote as an
alternative.
Peace ‘n love ‘n’ home made hummus,
P.
—
.
“We are not for names, nor men, nor titles of Government,
nor are we for this party nor against the other but we are
for justice and mercy and truth and peace and true freedom,
that these may be exalted in our nation, and that goodness,
righteousness, meekness, temperance, peace and unity with
God, and with one another, that these things may abound.”
(Edward Burrough, 1659 – from ‘Quaker Faith and Practice’)
Paul’s book, “Energy Beyond Oil”, is out now!
For details see https://www.fraw.org.uk/mei/ebo/
Read my ‘essay’ weblog, “Ecolonomics”, at:
https://www.fraw.org.uk/mei/ecolonomics/
Paul Mobbs, Mobbs’ Environmental Investigations
email – mobbsey@gn.apc.org
website – https://www.fraw.org.uk/mei/index.shtml
Gas in the UK (2)
…Continued from https://www.joabbess.com/2012/06/12/gas-in-the-uk/
Questions from the floor
[Tony Glover]
…increasing electricification of heat and transport. I was interested in what Doug said about heat. [If energy conservation measures are significant and there is] a significant reduction in gas use for heat…interested in the Minister’s response.
[Terry ? (Member of PRASEG)]
I’m interested in gas that would need CCS [Carbon Capture and Storage] [in future] …[since there would be no restriction there would be an] incentive to build new gas in next few years away from CCS-usable infrastructure. Maybe encouraging gas stations over next few years to be built in view of CCS.
[ ? ]
[There have been mentions of the] Gas [generation] Strategy and gas storage. Is it your intention to have both in the Energy Bill ? [Need to improve investor confidence.]
[Charles Hendry MP] I’m more confident than Doug on CHP…[in respect of energy conservation we will begin to increase our use of] CHP [Combined Heat and Power], geothermal energy, don’t need District Heating. I think we’ll see more people switch to electric heating. The likely pricing on gas will mean people have to look at other sources – such as localised heat storage, intelligent ways to produce hot water and heat in their homes […for example, a technology to store heat for several days…] The first [new gas power] plants will be where they are already consented – where originally coal plants – need to have identified in advance – no new plant is consented unless…We’ve asked Ofgem to ask re securing gas supplies. If we can stretch out the tail of North Sea gas – can stretch it out 30 – 40 years […] technology […] Centrica / Norway […] develop contracts […] Is there a role for strategic storage [Centrica asking] […] Buying and selling at the wrong price (like the gold) [widespread chuckling in the room]. Some of it may not need legislation. Gas Strategy will be published before the Energy Bill.
[David Cox] Get very nervous about gas storage. Don’t think there’s a need to put financial incentives in place to increase gas storage. We think the hybrid gas market is successful – a market and regulatory framework – [gas storage incentives] could damage.
[Doug Parr] I’m not downbeat because I want to be downbeat on heat. [Of all the solutions proposed none of them show] scaleability, deliverability. I’d love that to come true – but will it ? […] Heat pumps ? Biogas is great but is it really going to replace all that gas ? If we’re going to be using gas we need to make the best use of it […] Issues around new plant / replacement – all about reducing risks no exposing ourselves to [it] – security of supply, climate risks, issues about placement [siting of new plant]. If CCS can really be made to work – it’s a no-brainer – do we want all that carbon dioxide in the atmosphere or … ? Our entire policy becomes dependent on a technology that hasn’t even been demonstrated. Other technologies that people thought were great – years later they still haven’t arrived [for example, rooftop wind turbines]. If we say CCS is the only way it’s going to work – what’s Plan B ? We are going to use [fossil fuels] – should not become wholly dependent on technology not yet demonstrated.
[Alan Whitehead] Perhaps people should be asked – which would you prefer – a CHP / DH [Combined Heat and Power / District Heating] plant in the valley here, or a couple of wind turbines on that hill ? That would [shake things up].
Questions from the floor
[ X ? ] See […] as the ultimate destination. Most important – gas can be made zero carbon – not pie in the sky. 1. Start contributions of carbon-neutral gas and 2. will need far less if [we act] like Japan – force installation of microCHP. Their aim is to do same as for washing machines [bring prices down – make widely available for the home]. MicroCHP [with] heat pumps – reduction as good as decarbonising gas or electricity. But can also decarbonise gas.
[ X ? ] The Minister mentioned the importance of CHP but recently dropped […] mandate. If CHP so important what measures is the Government taking to ensure its installation ?
[ X ? ] Electricity is a rubbish fuel for heating buildings – very peaky load – need something cheap to store, cheap to […]. Fits very well with forcing down demand. Where we’re getting our gas from. At the moment our waste is being incinerated. For a cheap additional cost, where currently incinerating we can do anaerobic digestion [AD], producing a fungible asset – the gas – can gradually decarbonise our grid.
[ Thomas Grier ? ] …a decision [?] of London – CHP in London over the next few years. If we want to use electricity for heat, we need to reinforce the electricity grid [by 60% to 90% ?] In rural situations – use electrical heating. In urban, use decarbonised energy. [This model projection] shows the gas grid disappearing – it will collapse at some point if all we have on the gas grid is cooking.
[ X ? ] …[encouraged CHP then a few days later] stood up then said all support [removed ?] for CHP next year. A Heat Strategy that said there is enormous [scope / potential] for CHP. We want to see gas, we want to see efficiency. Are we moving towards […] without it they won’t build it.
[David Cox] Microgeneration – couldn’t get it down economically. Reliability [issues]. Full supporter of biogas – AD got a contribution to make – but never more than 5% – no matter how much [we crack it]. Electricity is not very good for heating – but how to we decarbonise the heat sector ? Always been an advocate of CHP. Government need to do more incentivising of that.
[Charles Hendry MP] Innovation and invention […] Government can’t support all emerging technologies. Best brains around the world [are working on] how we move fundamentally in a low carbon direction. On the waste hierarchy – burning of waste should be the final stage – finding a better use for it. [I visited] the biggest AD plant in Europe in Manchester – biogas and electricity generation. We are seeing Local Authorities taking a more constructive long-term view on how to manage waste. CHP – we all want to see more of it – to what extent does it need support ? That depends on whether new build – building a community around it. [By comparison, urban retrofitting is probably too expensive] Iceland [took the decision and] retrofitted almost every home – I’m now more convinced than before. What is the right level of subsidy and what makes good economic case ?
[Doug] We do keep missing opportunities. [For example in Wales, Milford Haven, the new Combined Cycle Gas Turbine at the Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) refinery to process the gas] should have been CHP. I am enthusiastic about lots of heat technologies [but the same questions/issues apply] scaleability and deliverability. District heating [DH] – an infrastructure asset ! [Can change priorities about what gets built – for example in Denmark (?)] they’re building large-scale solar farms to top up the DH. In the Treasury’s infrastructure plan [see DH could be…] Heat is the poor relation in energy debate. Other networks have been identified in the National Policy Statements (NPS) – but not heat.
[ Leonie Green, Renewable Energy Association ] [I must] defend heat pumps. In Sweden 90% of new builds [hav e heat pumps ?] – heat pump efficiency is a function of the energy-efficiency of the building […] Just on AD – National Grid report said it could provide 50% [of the nation’s supply. Our members think] that’s a bit too high – we think 25%. My question is really about the benefits. We are hearing anxiety about costs, but it’s piecemeal on benefits. We’ve been strong on jobs, balance of trade, exports [all benefits of renewable energy investment and deployment]. Pleased to see DECC put out [report from] Oxford Economics [on the] wider economic benefits. How can we get more and more balance in reports. [An example] Deutsche Bank renewable generation opportunities.
[ ? ] We would also support more than 5% from renewable gas – also about hydrogen – we used to do it when it was town gas – why not again ? As regards injecting biomethane/biogas from AD into the National Grid [last year ? to this year ?] 130 enquiries to connect AD to our network – none have progressed. Please sort these [registrations] out.
[ ? ] Minister, we’re not expecting you to fund all technologies – we need some logic – especially with transport. The Government doesn’t recognise the difference between Renewable Natural Gas if used in transport and fossil fuels. Would be simple – a tax on gas if used in a vehicle. What’s the problem over […] ?
[Colin Snape, University of Nottingham] We are looking at reducing the costs of carbon capture – we have a section of PhDs… One other gas source not mentioned – gas from underground gasification of coal [UCG]. In UK […] 2 billion tonners of coal – slightly offshore – on the energy coast of the UK – where all the action is on CCS – obviously UCG needs to be coupled with CCS to be carbon neutral. Would [be operational] in a very short time period […incentives…]. Significant proportion of UK needs.
[ ? ] What is the purpose of the Gas Strategy ? Shale gas isn’t a miracle. The “Golden Age of Gas” [report by the International Energy Agency (IEA)] doesn’t mean cheap gas, because [it will be put to] lots of uses. Renewable electricity and nuclear are not going to come until the 2020s. How do we avoid building loads of gas generation that is not necessary after that time ? What’s the role of mothballing (relatively cheap to bring CCGT out of mothballs comparing to build new). No sign of reduction in electricity demand reduction – therefore there will be high gas use.
[ Doug Parr ] On UCG, the IEA had two scenarios in the “Golden Age of Gas” – both took us over 3.5 degrees Celsius [in additional global warming]. Even if there is unconventional gas sources, still a huge danger of going down the road of unrestrained gas use. What is the alternative ? We should not end up becoming dependent on gas. Should not build gas to fill a short-term hole – they will lobby for their own interests – to keep open.
[ David Cox ] CCGTs won’t be built without guarantees greater than 20 years. Also renewable energy might not provide in the way that we hope. The CCC report – what caused the rise in energy prices ? The wholesale gas price – not renewable energy, green policies. However, that was slightly dishonest – the counter-factual was […] renewable energy significantly still more expensive than fossil fuel there. Until we can get costs of renewable energy down to the prices of fossil fuels… [The industry] don’t give the impression [they will build] on the basis of short-term need. Gas isn’t clean, I admit that […] CCS – that will work.
[Charles Hendry MP] A lot comes back to a need for a balanced approach – carbon targets and security of supply. If you haven’t sorted out security of supply, the electorate will not give permission to go low carbon. Gas is a hedging fuel currently but don’t know where costs going over time. As a politician, I like pipelines – know where it’s going (not like LNG, where there was limited use of new LNG import plant). If we want Scandinavian gas, we need security of demand to build the new pipeline. How we deal with issues of biomethane – in 2 years – need to make more progress. Some of these [techologies] will be gamechangers – some, look back in a couple of years… [Need a] permissive framework to allow a lot of ideas and technologies. There is no source of energy that hasn’t required subsidy in early days. Fanciful to suggest new forms of energy can come through without support. The letters we get [from the public, from constituents] are on vehicle fuel costs, not how much their gas bill went up last winter…
Official end of meeting
A gaggle of people gathered in the hallway to discuss some items further.
The Electricity Market Reform (EMR) was generally criticised – as it contains measures likely to specifically benefit nuclear power. Electricite de France was identified as very involved. The Government had said “no nuclear subsidy”, but the EMR measures are equivalent to hidden subsidies.
The Levy Cap was criticised as it would disturb investor confidence – if several nuclear reactors came on-stream in 10 years time, in the same year, they would eat up the whole subsidy budget for that year – and other technologies would lose out. If was felt that a number of the EMR proposals were “blunt instruments”, not overcoming shortcomings of former levies and subsidies.
Although the EMR was designed to addressed economic fears, it wasn’t assisting with financing risks – if anything it was adding to them. Rates of return have to be guaranteed for loans to be made – chopping and changing subsidies doesn’t allow for that.
Leonie Green said that the REA members don’t like the Premium Feed-in-Tariff (FiT). She also said later that they were not pleased about the cuts in support for AD.
Since my personal interest is in using Renewable Gas of various sources (including Biomethane / Biogas) to displace Natural Gas from the gas grid, I spoke with various people about this informally (including a woman I met on the train on my way home – who really got the argument about decarbonising gas by developing Renewable Gas, and using that to store excess renewable electricity, and use it as backup for renewable electricity. Although she did say “it won’t be done if it won’t confer benefits”.). One of the key elements for developing Renewable Gas is to create a stream of Renewable Hydrogen, produced in a range of ways. Somebody asked me what the driver would be for progress in Renewable Hydrogen production ? I said the “pull” was supposed to be the fabled “Hydrogen Economy” for transport, but that this isn’t really happening. I said the need for increased sources of renewably-sourced gas will become progressively clear – perhaps within a decade.
One of the persons present talked about how they think the Government is now coming out of the nuclear dream world – how only a few of the proposed new reactors will get built in the next decade – and how the Government now need to come up with a more realistic scenario.
It was mentioned that is appears that the Biogas technologies are going to have the same treatment as solar photovoltaics – some sort of subsidies at the start – which get cut away far too early – before it can stand on its own two feet. This was said to be the result of an underlying theory that only a fixed amount of money should be used on launching each new technology – with no thought to continuity problems – especially as regards investment and loan structures.
This Is My Thesis
I have recently been awarded a postgraduate Master of Science (MSc) degree, and several of my contacts suggested that I might consider studying for the academic qualification of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD). To be awarded a doctorate, I would need to make a valuable contribution to the body of knowledge and achievement in my chosen field. I do not think that paper-based research on its own would count as taking collective human understanding a step further, and so I must consider what forms of theorising, construction, engineering, creation, experimentation, configuration, data collection, analysis and argumentation I would need to make accomplishments in, in order to gain the good review of my peers, and the acceptance of my skill. It is not enough to love Wisdom, she has to be sought out, and introduced to your friends.
My first instinct is collaborative – how can I find a place where I can nurture my learning and strategy, in co-operation with others – where I can find a welcome, and make statements and discoveries that gain me a status, get me recognition ? I want to shine, in order to become useful, to serve my fellow woman and man. I don’t want to be competitive, winning out over others, but be part of a vanguard, a flight formation, spurring each other on to make progress together, striving as a group. I’m not ambitious, except for truth, beauty and good technology. I can share acclaim and I want to bring everybody with me. We can, standing elbow to elbow, vanquish destructive forces.
Yet, this proud, altruistic aim, to be part of the pack of pioneers, to offer something helpful, is marred by reality. Whilst I want to be constructive, others adopt divisiveness, in order to isolate outliers, and clamber over others to win the crown. I must not only reserve my right to speak against the herd, I must also wield it. I am relegated to the Zone of Insignificance, the people whose voices do not count because they articulate criticism. I do not want to join those who act as if they have the only viable formulation of reality – with their patronising stance – offering to host the public conversation, claiming they are at the centre of the debate, whilst at the same time undermining others with clever cynicism and sneering dismissal of those who will not join them.
I cannot be bought, and neither can I be seduced into a false alliance. I will not support meta-narrative, nor other contrivances. But this leaves me conflicted. One of the most significant problems with public discourse on science and technology in relation to resource limits and environmental damage is the persistence of the “anti” lobby – those people who feel bound to continue to be negative about things that have not yet been resolved. Many have been anti-nuclear, anti-fossil fuels, anti-coal, anti-energy companies, anti-Government policy, anti-hijacking of the United Nations process on climate change by economists. These voices, these positions, are important, but do not own the platform, and so they continue to rage. It is impossible to make progress without having something to rally around, to have a positive flag to muster under, but people with genuine influence continue to mis-step in their proposals and policies.
I want to bridge the gaps between the social groupings – I need to – in order to offer a way forward that can put some of the anti-thesis to bed, and galvanise efforts towards real, workable, cost-effective solutions. A genuine peoples movement for progress can accrete consensus, enormous non-hierarchical power, and can even draw in its detractors if it can be seen to be working. I am going to have to step out in faith, and at much risk – for I am going to attempt to join together the direction of the energy sector with the concerns of the environmentalists. I am not going to use a marketing strategy, nor sell a public relations pill to financiers and investment funds. I am not going to paint a green picture that has no details or exists only in a dream world. I am fairly certain that everybody is going to hate me, at least for a while, but in the end, I hope they will see that I am right, as I feel I am not generally mistaken.
Since I expect to be slighted and put down, and for people to work to marginalise me, I do not expect to be adopted by an academic institution or an energy or engineering company in the pursuit of my goals. In fact, I would resist such appropriation, for I am intellectually liberated. So, my work will not be accorded a standard accolade by a respectable institution or corporate body, and in fact, since that is the case, I can choose to work in any way that I see fit. Since, according to many scientists, we do not have much time to gain global assent for workable climate change solutions, as we must have a peak in greenhouse gas emissions in the near term, I cannot measure out five or seven years to complete a body of work which would then be reviewed. Instead, I shall publish in stages, and take peer review, including negative criticism, if any should be offered, as I go.
Although I wish to be practical rather than purely written, I shall not have much access to the funds, laboratories or engineering workshops where I could do the work myself. Instead, I shall have to ask questions of those who are already doing the work I am following, and try to ascertain their progress, and make my recommendations for their advancement. I seek to investigate live uses of the technology and systems I write about – as I expect them to be put to use before I have completed documenting them. My work will therefore be literature, but I want my intelligence to be fully accessible, so I will not use academic forms of composition. I shall write in what I hope is an easy, open way, and provide a mechanism for reply. I am going to offer my work by subscription, and I hope that those who register to receive my report in sections, will participate in making my work better.
The human race needs to be for something, not merely against, in all the myriad multitude of complaints that rise up like evaporating water, or steam from boiling pots, all and every day. However, a false unity, or a crooked one, cannot help us. We need to use what we’ve already got, and only imagine small gains in technological prowess. We should stop believing in public relations and advertising. We should stop being lulled into passivity by those glossing over our concerns, or those outspending logic. We should not give up in the face of overwhelming ineptitude and embedded vested interests. We cannot overhaul everything overnight, and somebody’s got to pay for change, and so they had better be the right changes. We need to be pragmatic, and not overreach, nor over-commit ourselves where technology could fail.
Moving towards a logical conclusion
 | |
| Although I consider him to be an enemy of the people by being a key architect of the privatisation of the UK’s National Health Service (NHS), I was delighted to hear Andrew Lansley say this about tobacco sales : “We don’t work in partnership with the tobacco companies because we are trying to arrive at a point where they have no business in this country.” Finally, after over ten years of hard work by a rainbow coalition of healthcare providers, local government administration, campaigners, social activists, educators and charities, it is possible for the UK Secretary of State for Health to tell the tobacco industry their products are not wanted here.
The deep question is : why didn’t the UK Government just ban the tobacco companies outright at the start or tell them to diversify out of selling cancer sticks in order to keep their retail licences ? Well, the simple answer is that companies like British American Tobacco (BAT) are privately-owned capitalised companies, with many pension and other major funds heavily invested. The UK Department of Business, Trade, Enterprise, Industry, Information, Skills, Services and Manufacturing or whatever it’s been variously called over the last few decades, simply couldn’t tell shareholders to pull their investment out of death-by-inhalation stocks. Everyone sees a return on investment in the industries of death generally, such as the arms trade, the junk food industry, and petrochemicals (ask yourself : how many people have suffered and died because of diesel particulate-provoked asthma ?) It takes a certain amount of time to reach the logical conclusion that wars do not need to be fought, making armaments redundant; for healthy food to become seen as essential to beat off diabetes and obesity epidemics; and for urban transport to be electrified to save lungs and hearts. No, you just can’t ban an entire product range overnight because, finally, the science has broken through the doubt barrier and shown beyond reasonable scepticism that tobacco smoking causes cancer, emphysema and other serious and fatal conditions. No, you have to go at it step by painful step, reducing availability, changing the rules on presentation at the point of sale, putting up signs in public places. And it all takes time, this gradualist approach. The tobacco industry may now wind down to a dribble in Britain (although it will continue to do well in Asia and Africa), and peoples’ savings for retirement will have soon all moved out of fag ends into something else. Yet, we don’t have the luxury of time when it comes to the climate change and energy crisis. We simply don’t have the 25 to 50 years it could take to adopt a gradualist approach to energy sector change. Anything that takes longer than 10 years to begin to displace carbon out of the energy economy is too slow to be useful. People are slowly beginning to wake up to the fact that their money is invested in climate change, and are making demands on their pension fund and bank account managers – but this is all happening too slowly – despite the keen interest in ethical investment. The energy sector has got to change – and change fast. Changing the energy sector so radically and so quickly is not something that can be done by applying small changes to the costs of energy – particularly as the wider costs of energy are so volatile anyway. Gradually introducing renewable energy technologies with subsidies and grants and special tax breaks is not going to displace carbon fast enough. Governments may not like the thought – but maybe they will consider starting to ban things – and not be shy about being explicit. However, this kind of action will generate significant resistance and dissent. How then to rapidly alter the world’s entire energy sector ? Start telling the truth about how the energy sector is scraping the bottom of the barrel in a number of fuels and fields ? Could this approach cause a run at the investment bank ? Could it tip the balance in energy systems deployment towards the less-intensive options – green energy – the only possible area of growth in the energy sector – which becomes the only possible logical conclusion ? | |
On Being Climate Pragmatic
|
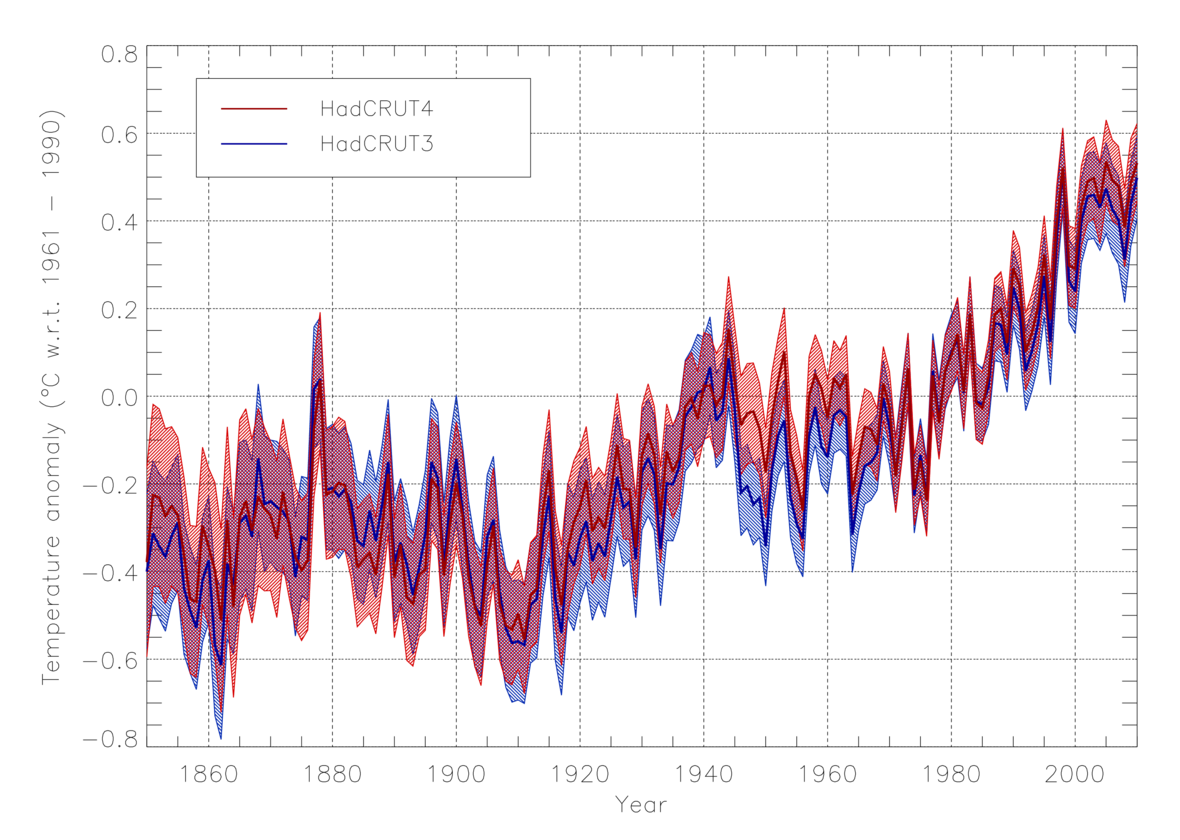
And the people cried “Let my data go !” And lo, it came to pass, that the time came for the UK’s Met Office’s Hadley Centre’s new HadCRUT4 near surface temperature analysis data set to be born online.
And across the land, the people wielded Excel spreadsheets and the like in the quest for visual engagement with the hot new numbers. |
| And it was seen that the year 2010 was hotter than 1998, and a number of other years in between were similarly warmer than 1998, and many climate change sceptics who had been so withering in their blanket denial of global warming quaked in their doubtful boots.
Interestingly, trends could be seen in the global averages, and so a linear trendline was plotted :- |
|
 |
This article was written by M. A. Rodger and was originally posted at DeSmogBlog and is syndicated by an informal agreement and with the express permission of both the author and DeSmogBlog, without payment or charge. |
| The previous post in this series examined the Global Warming Policy Foundation (GWPF) Briefing Paper No3 “The Truth About Greenhouse Gases“. Despite its title, Briefing Paper No3 said very little about such gases. Yet one subject (not directly to do with greenhouse gases) was discussed at some length within the paper. As it is also discussed in other GWPF papers, the subject will be examined in this fourth post of the series.
AN IMPOSSIBLE HOCKEY STICK AVERSION This series of posts (1, 2, 3, 4) examines the UK-registered educational charity & climate-change denying think-tank the Global Warming Policy Foundation (GWPF). This fifth post examines one of the assertions made within GWPF Briefing Paper No1. The paper boldly claims that the findings of the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (UN IPCC) are too narrow and that the work of “many scientists” is being ignored. Can it be true ? Is there “an alternative (scientific) view“ being overlooked by the IPCC ? This would be a monumental discovery ! Forget Briefing Paper No1. Let's examine those overlooked scientists. |
|
 |
I expect a number of my readers are objecting to my claim that global warming is accelerating. “Look,” they might say, “you’ve drawn a conclusion based on only two sample time periods, and you’ve only been able to show a gradual, linear rising trend for each of them. You’ve haven’t shown any evidence for an exponential curve !” |
| Well, yet’s it’s true, I only presented the evidence that it appears that there is a linear (straight) rising trend in global average temperature in the periods 1970 to 2011 and 1915 to 1945. And show that the rising trend is steeper in the period 1970 to 2011 than in the period 1915 to 1945.
What I have not yet done is give a bit of perspective. You see, in historical, geological terms, recent temperature rises are on the steep part of an exponential curve – so steep and so sharp that they appear to be in a straight line. |
|